Experimental Analysis to Control Welding Deformation in Thin Plate
Shipbuilding industries facing the problem of welding deformation for seven decades and trying to control this problem but the thin plates bring non-linear problems in the ship structure. Especially in the bulkhead of the ship structure that leads to welding deformation due to small members of the profiles. Mostly, the problem occurs in the construction of yachts building because clients need good outlook of the ship. Therefore, the development of a new effective method to
reduce the welding deformation in the thin plate by optimization of welding sequences and plating method at the time welding process and this method is help to reduce the deformation and also help to increase the productivity of the shipbuilding process.
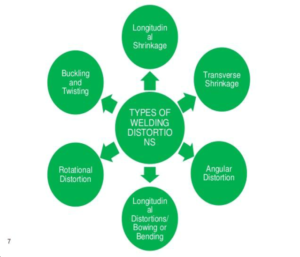
Welding is a process to join metals with different arrangements of the plates. Welding induced the distortion in the thin plate. There are six types of welding distortion:
The objective of this research to analyse the welding deformation, welding deformation is caused by the welding distortion; the main factor of welding distortion
is based on the following parameters which are given below:
- Longitudinal Shrinkage
- Transverse Shrinkage
- Angular Distortion
- Bowing and dishing
- Buckling
- Twisting
After welding the shrinkage is towards the weld axis longitudinally is known as “Longitudinal Shrinkage”.
After welding the shrinkage is towards the weld axis longitudinally is known as “Transverse Shrinkage”.
“Angular distortion” is the change in the shape of the plate by the welding. Consider the But welding in which the top part of the welding is wider than the bottom part.
As we know that two or more than two distortions will occur at the same time when longitudinal Shrinkage occurs then there will be the bending of the plate. That`s why is known as “Bowing”. This type of Distortion happens when the weld line and Neutral Axis of the structure do not coincide.
Mostly “buckling” is occurring in the thin plate. This type of distortion occurs away from the welding area this is due to the residual stress.
“Twisting” has also happened in the thin plate this is due to the low torsional resistance. Twisting of the plate occurs when the welding is done along the centre of the member. Due to this reason, the area tends to shrink and become shorter.
To read the full paper click here
